At AHVC (Asian Heart & Vascular Centre) we work closely with our neurology colleagues to treat patients. This is because some of these strokes can originate from the heart. This accounts for 20% of ischemic strokes. We call this condition cardioembolic stroke.
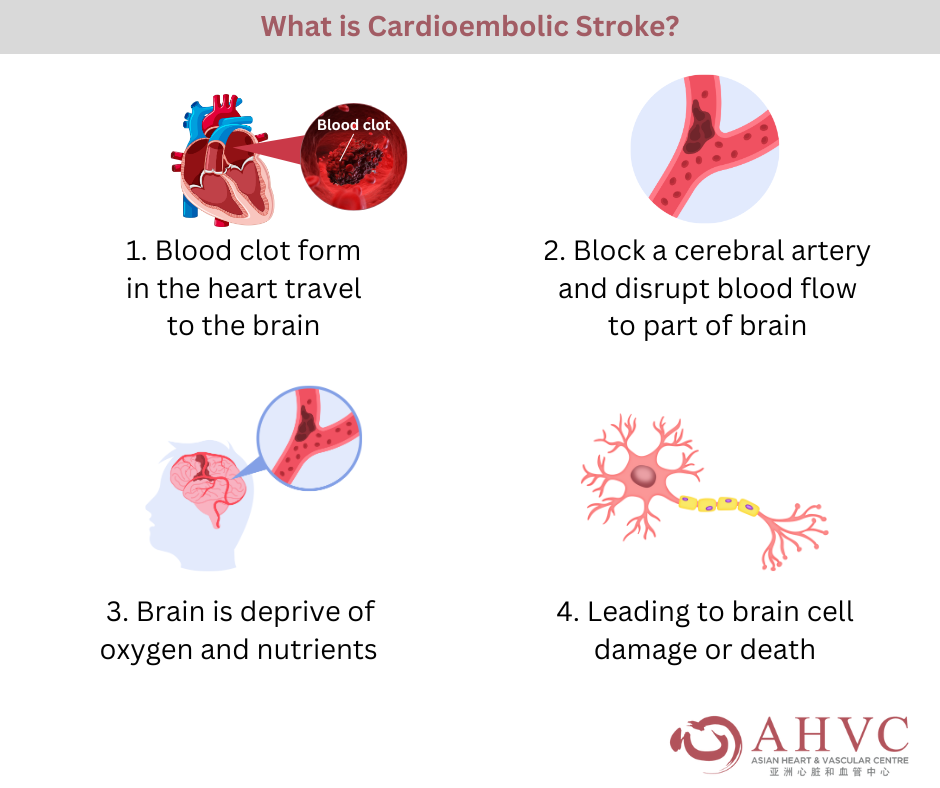
With cardioembolic stroke, blood clot that forms in the heart can travel to the brain, blocking a cerebral artery. This blockage disrupts blood flow to a part of the brain, depriving it of oxygen and nutrients, leading to brain cell damage or death.
The four main causes are:
- ‘Hole in the heart’
- Irregular heart beat (Atrial fibrillation)
- Heart valve disease
- Heart muscle disease/heart failure

‘Hole in the heart’ – Patent Foramen Ovale (PFO)
A Patent Foramen Ovale (PFO) is a tiny hole in the heart that didn’t close after you were born. It’s like a flap between two chambers of the heart that usually shuts when babies are born, but for some people, it stays open.
Now, this little flap usually doesn’t cause any problems. But sometimes, a small blood clot that would normally get filtered out by the lungs sneaks through this hole and goes to the brain. When this happens, it can block the blood flow to a part of the brain, which causes a stroke. A stroke happens when the brain doesn’t get enough oxygen because of the blocked blood flow, and that part of the brain stops working properly.

We can treat PFO and strokes in a couple of ways. One way is by giving medicine like blood thinners, which help prevent clots from forming. If someone keeps having strokes because of their PFO, doctors might recommend a procedure to close the hole. They do this by threading a tiny device through a blood vessel in the leg up to the heart to close the PFO. This way, blood clots can’t sneak through the hole and cause more strokes!

Irregular heart beat (Atrial fibrillation)
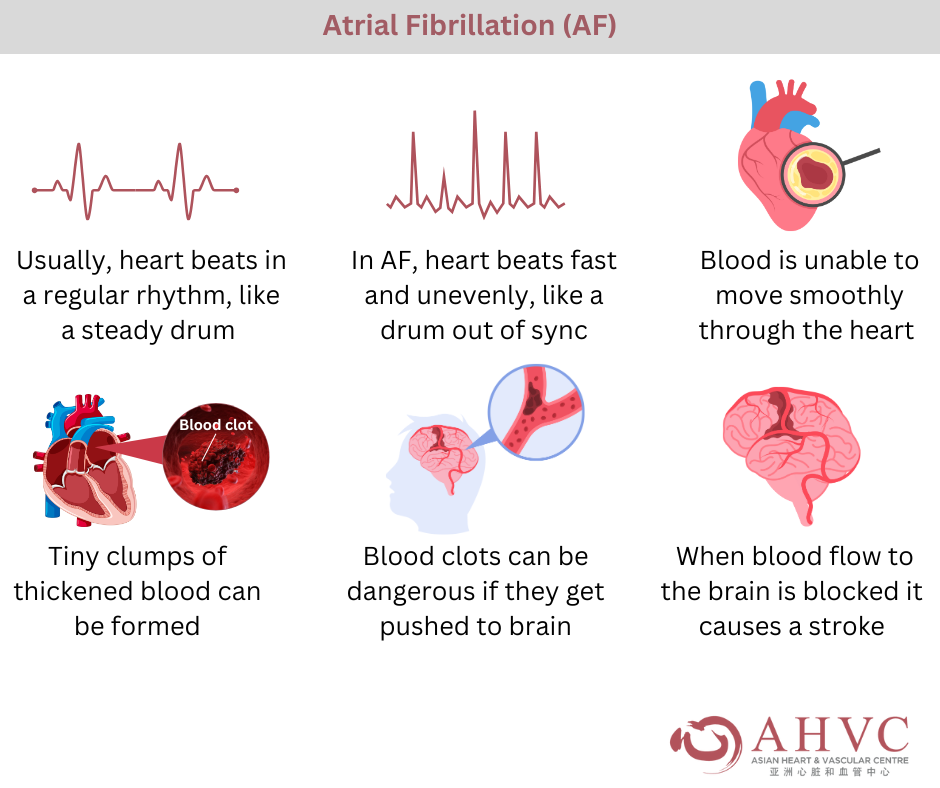
Atrial Fibrillation (AF) is a problem with the way the heart beats. Normally, the heart beats in a regular rhythm, like a steady drum. But in AF, the heart beats fast and unevenly, like a drum that’s out of sync. This makes it harder for blood to move smoothly through the heart, and sometimes the blood sits still for too long in one part of the heart.
When blood doesn’t flow well, it can form clots, which are like tiny clumps of thickened blood. These clots can be dangerous if they get pushed out of the heart and travel to the brain. If a clot blocks the blood flow to the brain, it causes a stroke, which means part of the brain stops getting the oxygen it needs to work.
To treat AF and prevent strokes, doctors use medicines called blood thinners. These make it harder for clots to form in the heart. Sometimes, doctors also use medicine or special procedures to help the heart beat normally again. In some cases, they might do a procedure called ablation to stop the areas of the heart that are causing the irregular rhythm. This way, the heart can pump blood smoothly and lower the risk of clots and strokes.
Some patients cannot tolerate blood thinners. In these cases, special umbrellas like devices are placed in the heart to prevent clots from going to the brain.

