Introduction
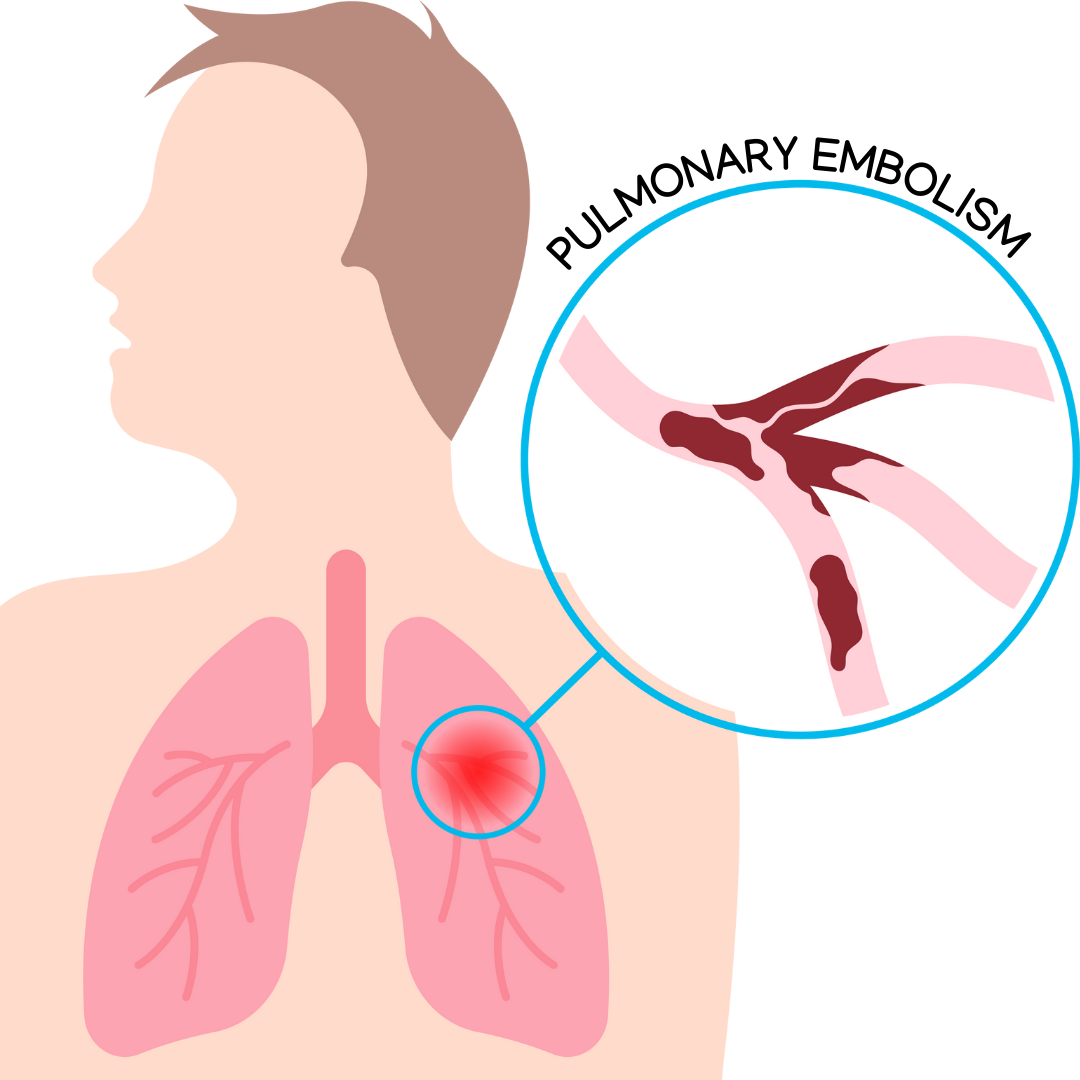
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a life threatening condition that happens when a blood clot blocks blood flow to the lungs. This can be dangerous and requires immediate medical attention. These clots usually come from the legs and travel up to the lungs, making it hard to breathe and causing chest pain.
What Causes It?
PE usually happens because of a blood clot that forms in the legs (called deep vein thrombosis or DVT). Some things that increases the risk of a clot include:
- Sitting or lying down for too long (eg. long flights or bed rest)
- Certain health conditions like cancer or heart disease
- Pregnancy or using birth control pills
- Obesity or smoking
- Family history of blood clots
- Having surgery, especially lower limb surgeries
Common Symptoms
Symptoms of PE depend on how big the clot is and how healthy you are. Some common signs include:
- Sudden shortness of breath
- Chest pain, especially when breathing deeply or coughing
- Fast heartbeat (tachycardia)
- Coughing up blood
- Feeling dizzy or faint
- Swelling and pain in one leg (a sign of a clot in the leg, associated with DVT)
How Is It Diagnosed?
Doctors use different tests to find out if you have PE, such as:
- Blood test – Checks for signs of clotting.
- CT scan – A special X-ray to see if there is a clot in your lungs.
- Ultrasound of the legs – Looks for blood clots in your legs.
Treatment Options
The goal of treatment is to stop the clot from getting bigger and prevent new ones from forming. Some common treatments include:
- Blood thinners – Medicines that prevent new clots and help existing ones dissolve over time.
- Clot-busting drugs – Used in emergencies to quickly dissolve large clots.
- Thrombectomy -Using a catheter like a big straw to suck out all the clots – minimally invasive but allows for the quickest recovery
- Caval filter – A small temporary device placed in the main vein of the body to stop clots from reaching the lungs if patients are unable to take blood thinners
How to Prevent PE
There are steps you can take to lower your risk of PE, such as:
- Moving around regularly, especially during long trips or after surgery
- Wearing compression socks to improve blood flow in your legs
- Taking prescribed blood thinners if you’re at high risk
- Maintaining a healthy weight and not smoking
Conclusion
Pulmonary embolism is a serious but preventable condition. Knowing the signs and risk factors can help you get medical help quickly. If you ever experience sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, or leg swelling, seek medical attention right away.